Living with blindness can present numerous challenges, but advancements in technology have opened up a world of possibilities for blind individuals. Assistive technologies have revolutionized the way visually impaired people interact with their surroundings, providing them with increased access to education, health services, and employment opportunities. In this blog post, we will explore some of the remarkable assistive technologies that are empowering blind individuals and helping them overcome barriers.
- Screen Reading Software:
One of the most crucial technologies for blind individuals is screen reading software. This software utilizes synthetic speech or Braille output to convert on-screen text into an audible or tactile format. It enables blind individuals to access digital content, such as websites, documents, and emails, making educational resources, job applications, and online services more accessible than ever before.
- Refreshable Braille Displays:
Refreshable Braille displays are tactile devices that convert digital text into Braille characters, allowing blind individuals to read electronic content through touch. These displays use a series of tiny pins that rise and fall to form Braille letters, giving blind users real-time access to digital information. Refreshable Braille displays have significantly enhanced educational opportunities and improved the efficiency of blind individuals in various professional fields.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
OCR technology plays a crucial role in making printed materials accessible to blind individuals. With OCR, printed text is converted into digital text, which can then be read aloud by screen reading software. This technology enables blind individuals to access printed books, documents, and even handwritten notes by scanning them with a dedicated OCR device or a smartphone app. OCR has revolutionized the way blind individuals access information, enhancing their educational experiences and facilitating independent living.
- Navigation and Wayfinding:
Assistive technologies have also revolutionized navigation and wayfinding for the blind. GPS-enabled devices and smartphone applications equipped with voice guidance provide real-time information about the user’s location, nearby points of interest, and turn-by-turn directions. Additionally, indoor navigation systems, utilizing technologies like Bluetooth beacons, assist blind individuals in navigating complex indoor environments such as airports, shopping malls, and train stations. These technologies empower blind individuals to travel independently and access public spaces with greater confidence.
- Assistive Apps and Devices:
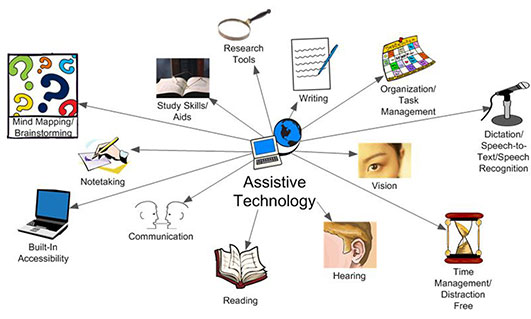
There is a wide range of mobile applications and devices designed specifically to assist blind individuals in various aspects of their lives. These apps and devices offer features such as object recognition, color identification, currency identification, and text-to-speech capabilities. They help blind individuals perform daily tasks independently, such as identifying objects, managing finances, and reading labels or instructions.
Living with blindness can present numerous challenges, but advancements in technology have opened up a world of possibilities for blind individuals. Assistive technologies have revolutionized the way visually impaired people interact with their surroundings, providing them with increased access to education, health services, and employment opportunities. In this blog post, we will explore some of the remarkable assistive technologies that are empowering blind individuals and helping them overcome barriers.
- Screen Reading Software:
One of the most crucial technologies for blind individuals is screen reading software. This software utilizes synthetic speech or Braille output to convert on-screen text into an audible or tactile format. It enables blind individuals to access digital content, such as websites, documents, and emails, making educational resources, job applications, and online services more accessible than ever before.
- Refreshable Braille Displays:
Refreshable Braille displays are tactile devices that convert digital text into Braille characters, allowing blind individuals to read electronic content through touch. These displays use a series of tiny pins that rise and fall to form Braille letters, giving blind users real-time access to digital information. Refreshable Braille displays have significantly enhanced educational opportunities and improved the efficiency of blind individuals in various professional fields.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
OCR technology plays a crucial role in making printed materials accessible to blind individuals. With OCR, printed text is converted into digital text, which can then be read aloud by screen reading software. This technology enables blind individuals to access printed books, documents, and even handwritten notes by scanning them with a dedicated OCR device or a smartphone app. OCR has revolutionized the way blind individuals access information, enhancing their educational experiences and facilitating independent living.
- Navigation and Wayfinding:
Assistive technologies have also revolutionized navigation and wayfinding for the blind. GPS-enabled devices and smartphone applications equipped with voice guidance provide real-time information about the user’s location, nearby points of interest, and turn-by-turn directions. Additionally, indoor navigation systems, utilizing technologies like Bluetooth beacons, assist blind individuals in navigating complex indoor environments such as airports, shopping malls, and train stations. These technologies empower blind individuals to travel independently and access public spaces with greater confidence.
- Assistive Apps and Devices:

There is a wide range of mobile applications and devices designed specifically to assist blind individuals in various aspects of their lives. These apps and devices offer features such as object recognition, color identification, currency identification, and text-to-speech capabilities. They help blind individuals perform daily tasks independently, such as identifying objects, managing finances, and reading labels or instructions.
Conclusion:
Assistive technologies have transformed the lives of blind individuals, providing them with unprecedented access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Through screen reading software, refreshable Braille displays, OCR technology, navigation aids, and a plethora of assistive apps and devices, blind individuals can overcome many barriers that were once insurmountable. However, it is important to continue developing and improving these technologies to ensure that blind individuals can fully participate in all aspects of society. By supporting organizations like “Battle For Blindness” and promoting the use of assistive technologies, we can work together to create a more inclusive world for everyone.





